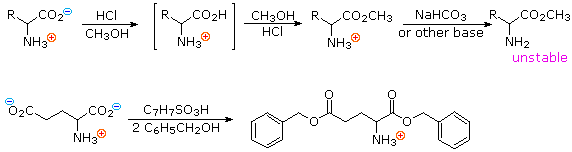
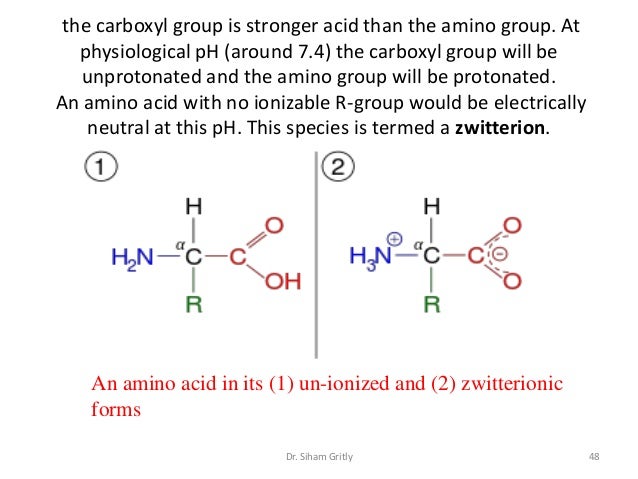
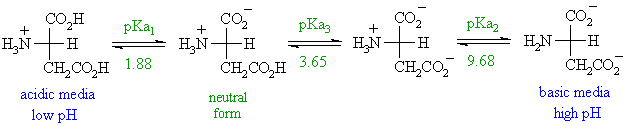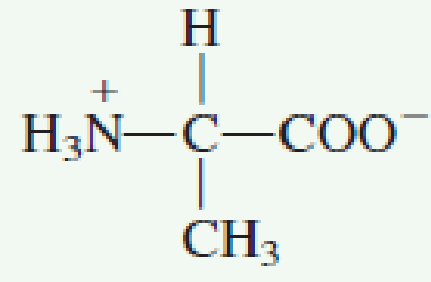L Amino Acid In Zwitterion
In chemistry a zwitterion ˈ t s v ɪ t ə ˌ r aɪ ə n tsvit ə rye ən.
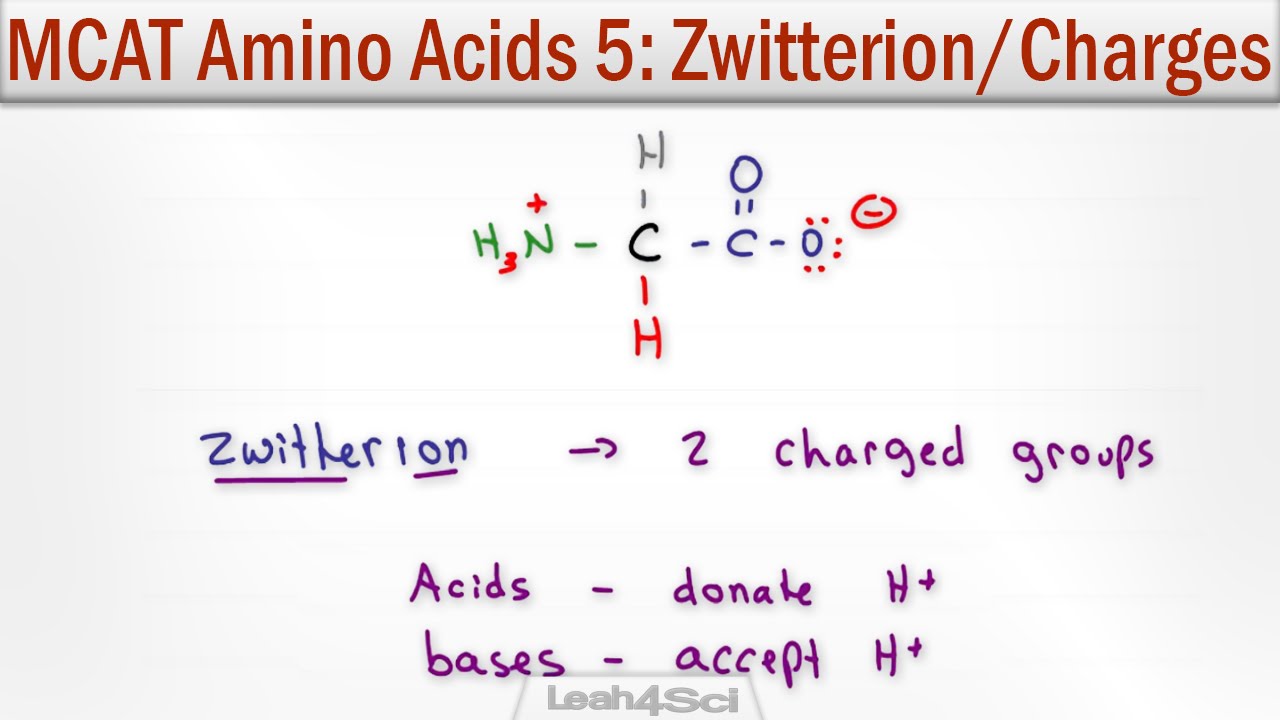
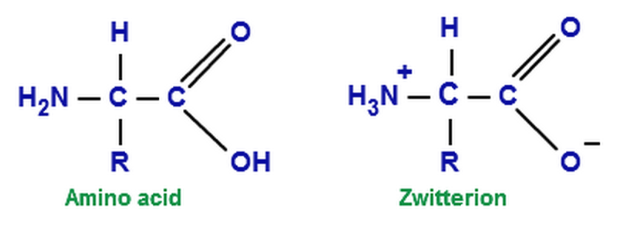
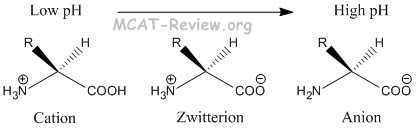
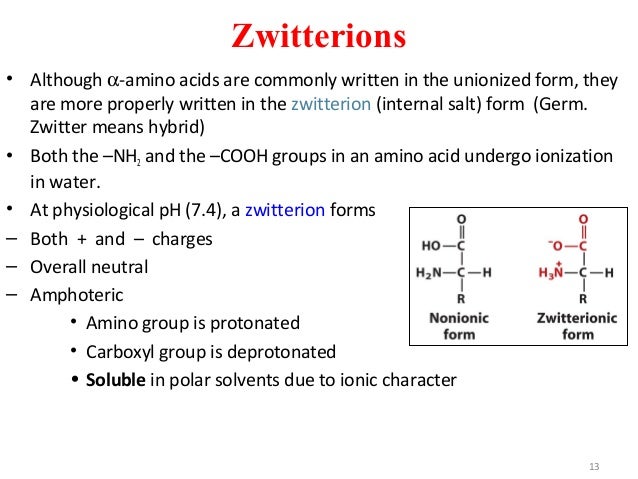
L amino acid in zwitterion. From german zwitter hermaphrodite also called an inner salt is a molecule that contains an equal number of positively and negatively charged functional groups. The r group represents the side chain of different amino acids. Zwitterions in simple amino acid solutions. A zwitterion by definition is a molecule with 2 zwitter ions one positive and one negative for a net zero charge.
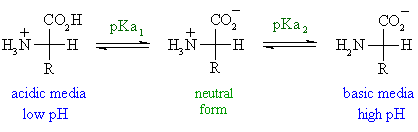
An amino acid has both a basic amine group and an acidic carboxylic acid group. The ratio of the concentrations of the two isomers is independent of ph. Amphoteric molcules are not necessarily zwitterionic. L and d amino acids are the two isomeric forms of amino acids which occur in nature.
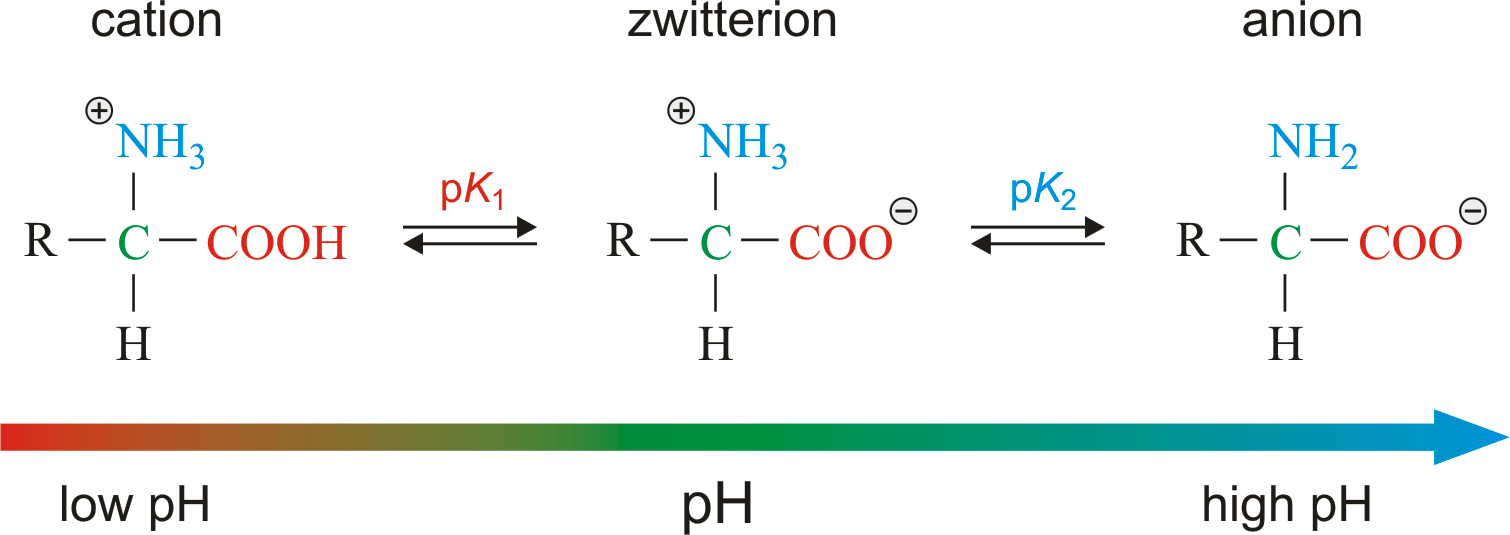
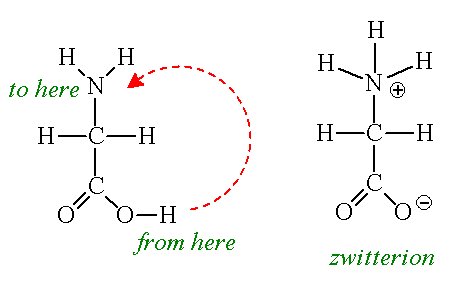
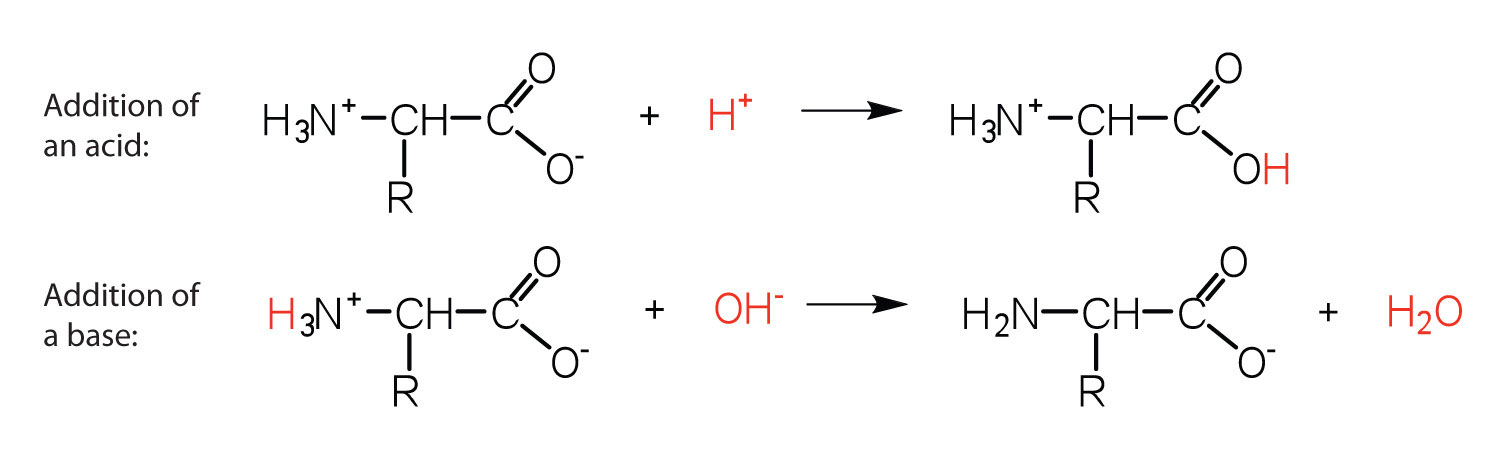
The amino group of an. Note the diprotic amino acid alanine. While neutral the zwitterion form of an amino acid will have a positive and a negative charge. There is an internal transfer of a hydrogen ion from the cooh group to the nh 2 group to leave an ion with both a negative charge and a positive charge.
In aqueous solution amino acids exist in two forms as illustrated at the right the molecular form and the zwitterion form in equilibrium with each other. The ph can affect the charge of a molecule by introducing protons h. A zwitterion is a molecule with functional groups of which at least one has a positive and one has a negative electrical charge. With amino acids for example in solution a chemical equilibrium will be established between the parent molecule and the zwitterion.
The main difference between l and d amino acids is that the amine group of l amino acids occurs in the left hand side when drawn in the fischer projection keeping the carboxylic acid group on top and the carbon chain in the bottom whereas the amine group of the d amino acids occurs in the right. This is the zwitterion form of an amino acid. Amino acids are the best known examples of zwitterions. Zwitterions and amino acids.
Amphoteric property amino acids are amphoteric in nature that is they act as both acids and base since due to the two amine and carboxylic group present. The neutral zwitterion is the usual form amino acids exist in solution. This video shows you how to quickly calculate amino acid charge at any given ph by helping you recognize when a given side chain is protonated or deprotonated. Amino acids exist as zwitterions at physiological ph.
The isoelectric point is the ph at which a zwitterion is uncharged. They contain an amine group basic and a carboxylic group acidic. Amino acids as zwitterions. The net charge of the entire molecule is zero.
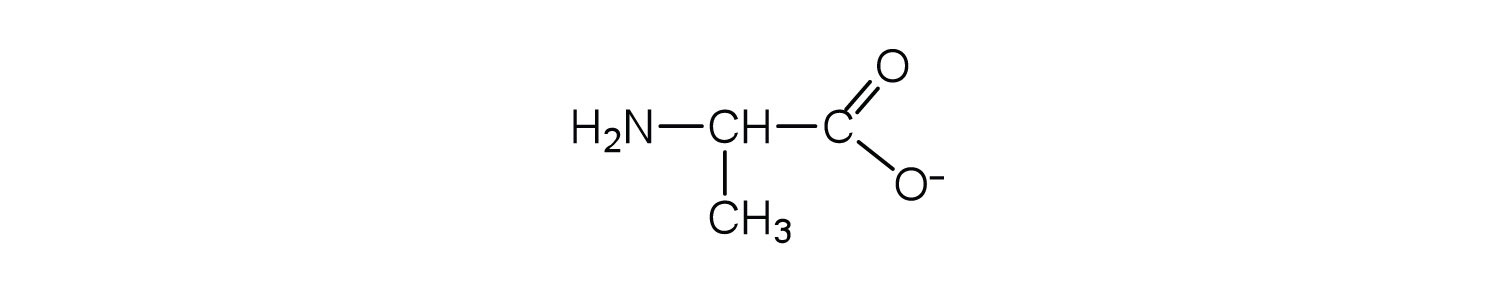
The standard structure contains both a carboxyl and an amine in the backbone. The zwitterion form of an amino acid is shown below. Therefore at ph 7 4 l ala is zwitterionic. The two forms coexist over the ph range pk 1 2 to pk 2 2 which for glycine is ph 0 12.
This is called a zwitterion.