A Site Ribosome
Pepityde site contains the peptide trna e site.
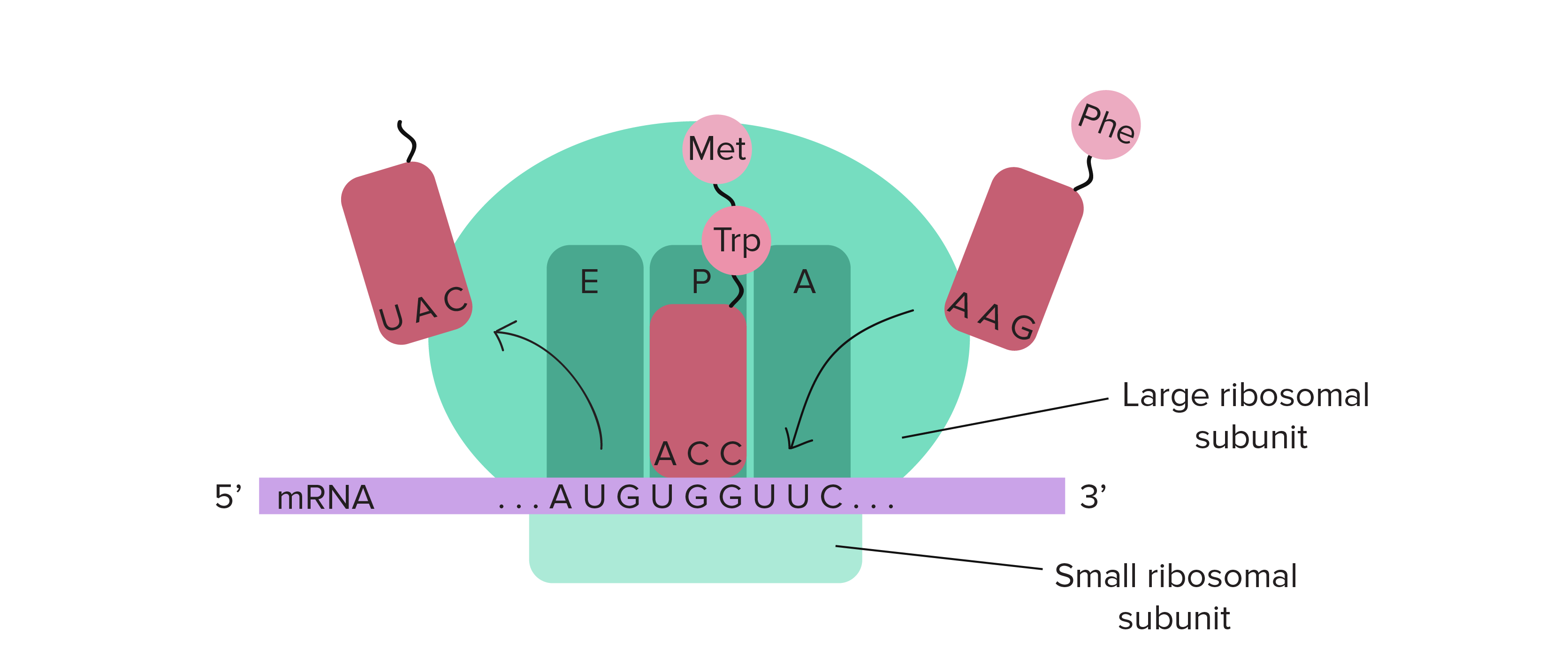
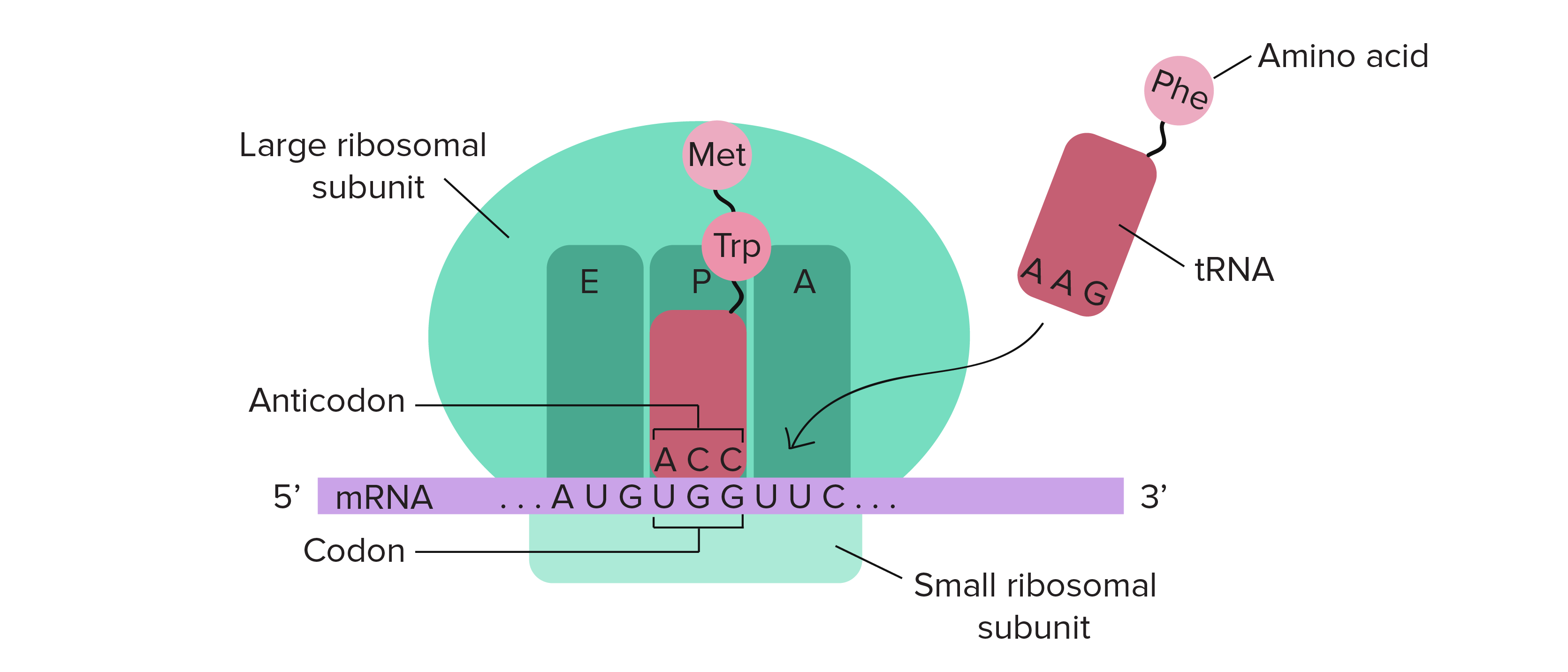
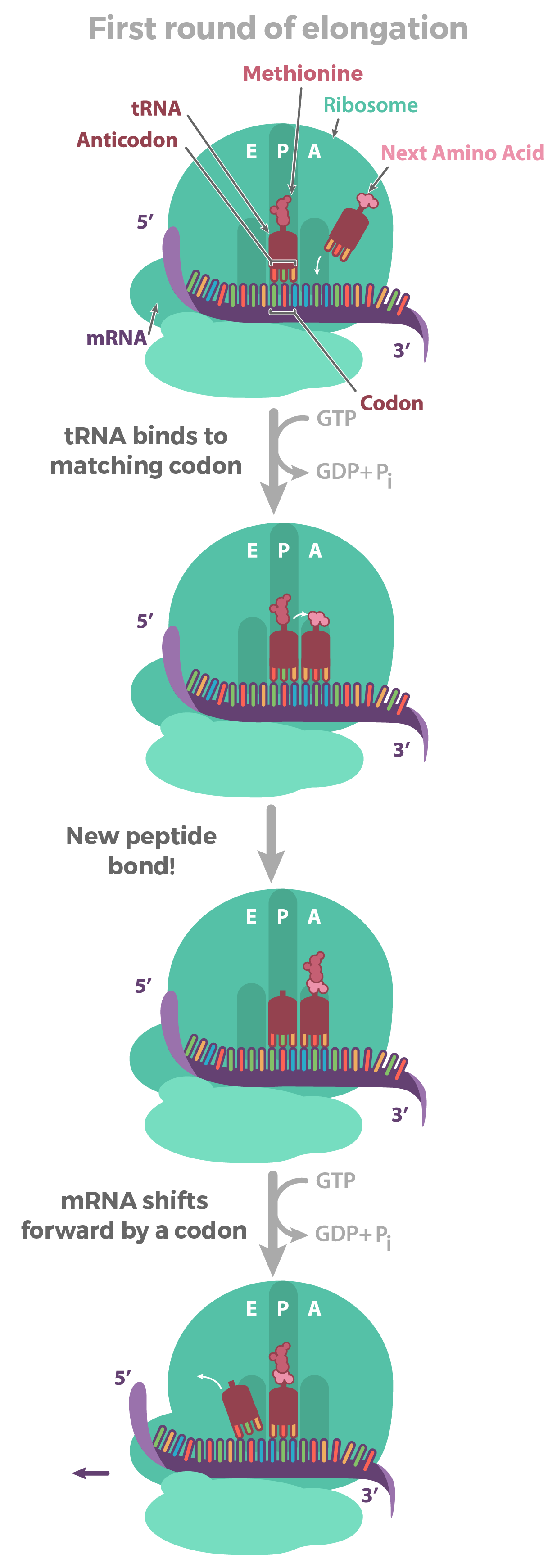
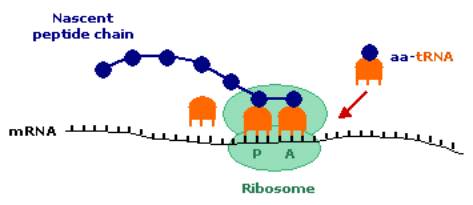
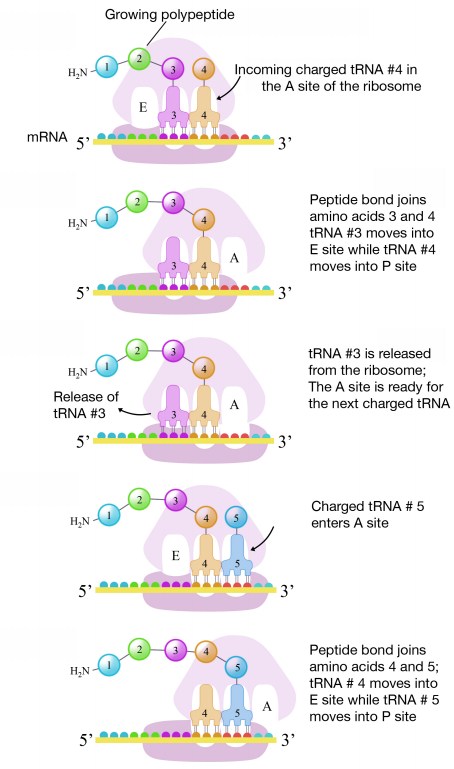
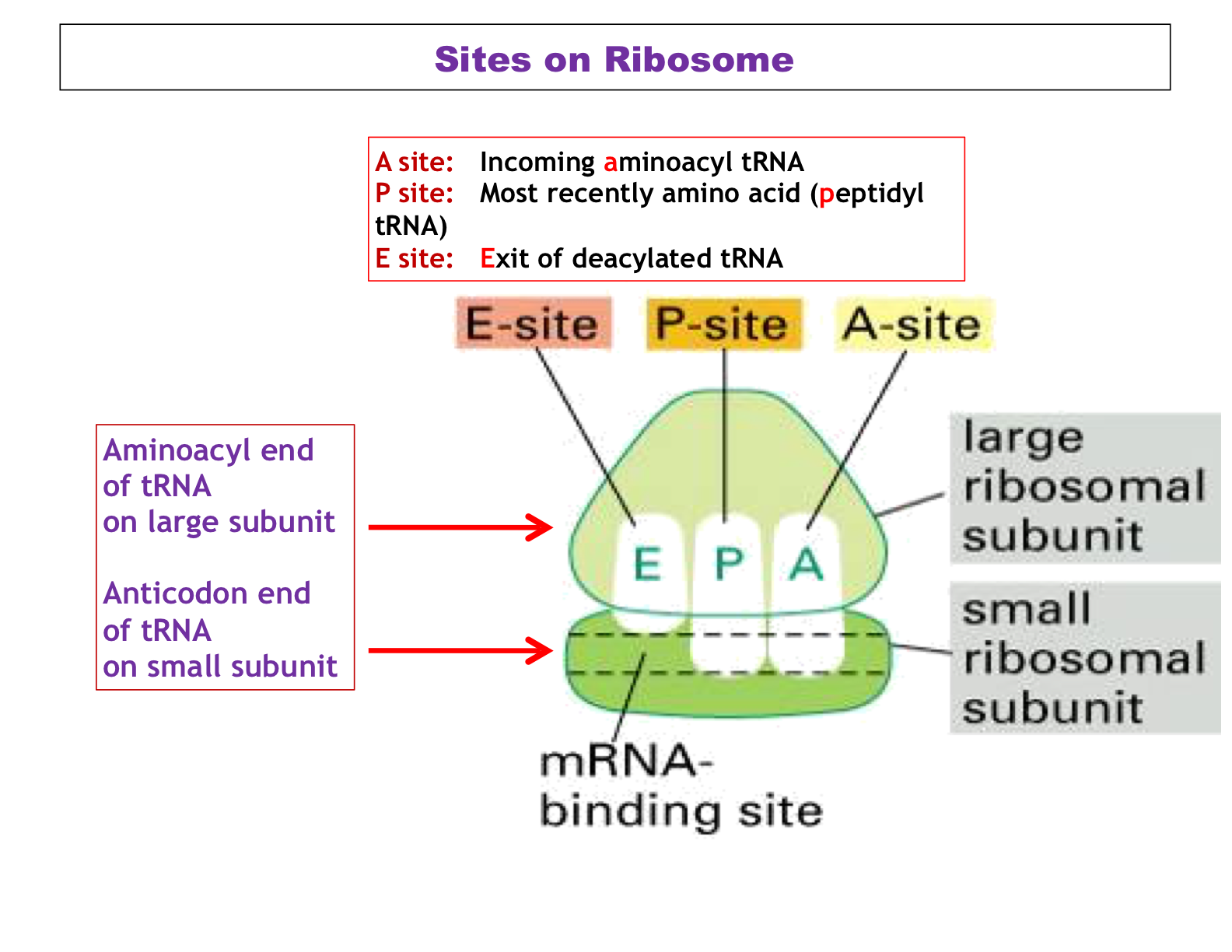
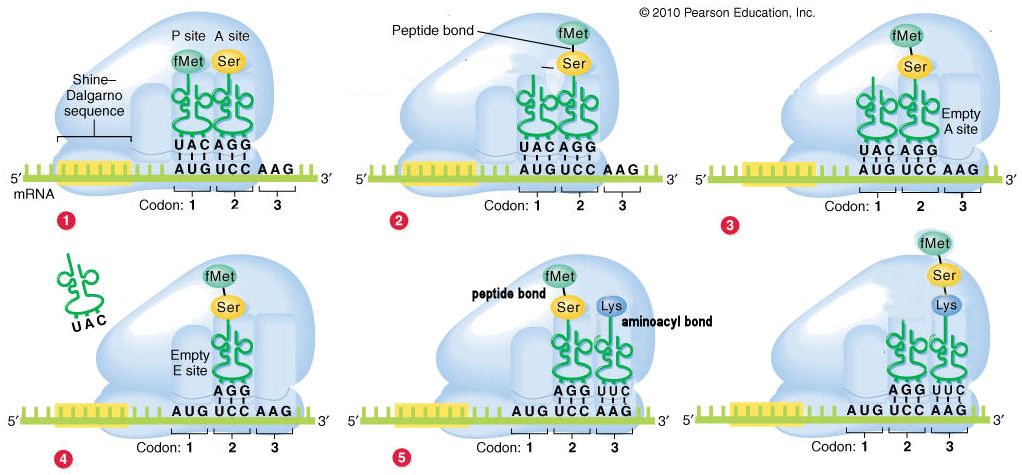
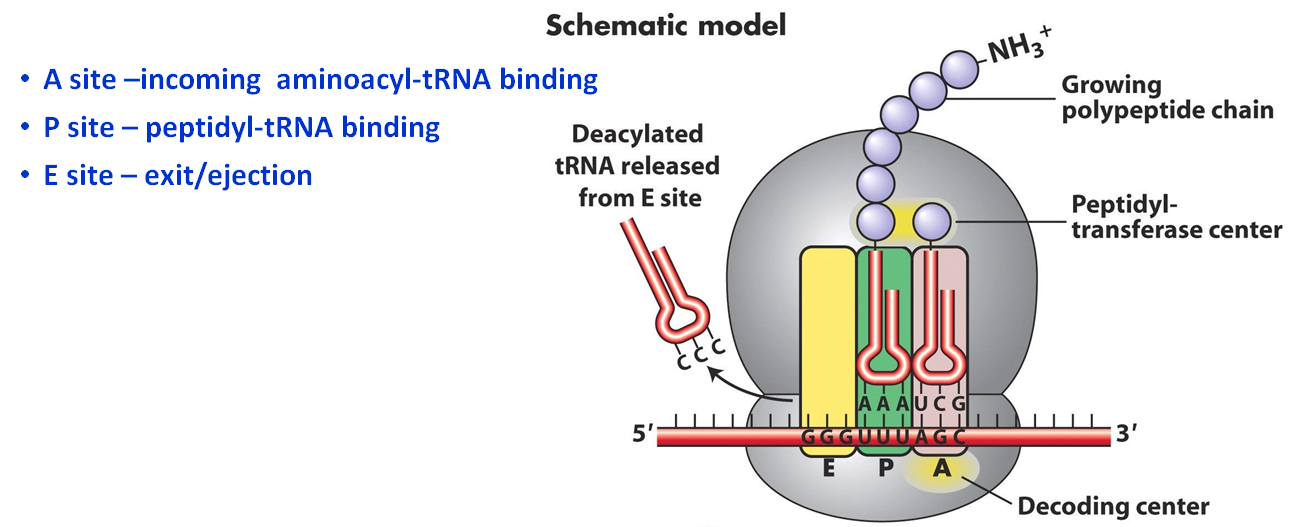
A site ribosome. Peptidyl trna binding or p site 3. Ribosomes link amino acids together in the order specified by the codons of messenger rna mrna molecules to form polypeptide chains. They are the aminoacyl site abbreviated a the peptidyl site abbreviated p and the exit site abbreviated e. Four binding sites are located on the ribosome one for mrna and three for trna.
The three trna sites are labeled p a and e. Trna exit site or e site structure of the ribosome. Acceptor site where incoming charged trnas bind p site. Exit site transiently occupied by uncharged trna on interface of the 30s and 50s subunits.
Ribosomes are composed of two subunits one small and one large. With respect to the mrna the three sites are oriented 5 to 3 e p a because ribosomes move toward the 3 end of mrna. The small and large ribosomal subunits. The three trnas bound to the ribosome are indicated in m.
The a site a for aminoacyl of a ribosome is a binding site for charged t rna molecules during protein synthesis. The three trna binding sites in ribosomes typically refer to. Each subunit consists of one or more ribosomal rna rrna molecules and many ribosomal proteins rps or r proteins. The left trna the a site has the amino acid that will be added the central trna the p site holds the growing protein chain and the right trna the e site is finished with its job and is ready to be ejected.
Aminoacyl trna binding or a site 2. The ribosome has three sites for trna to bind. In the center structure 4v5d three trna molecules are bound inside the ribosome. One of three such binding sites the a site is the first location the t rna binds during the protein synthesis process the other two sites being p site peptidyl and e site exit.
The order of trna molecules ultimately determines the amino acid sequence of a protein. Ribosomes are the sites at which information carried in the genetic code is converted into protein molecules.