2 5 Factorial Design Table

A 2 2 factorial design involved two factors a and b.
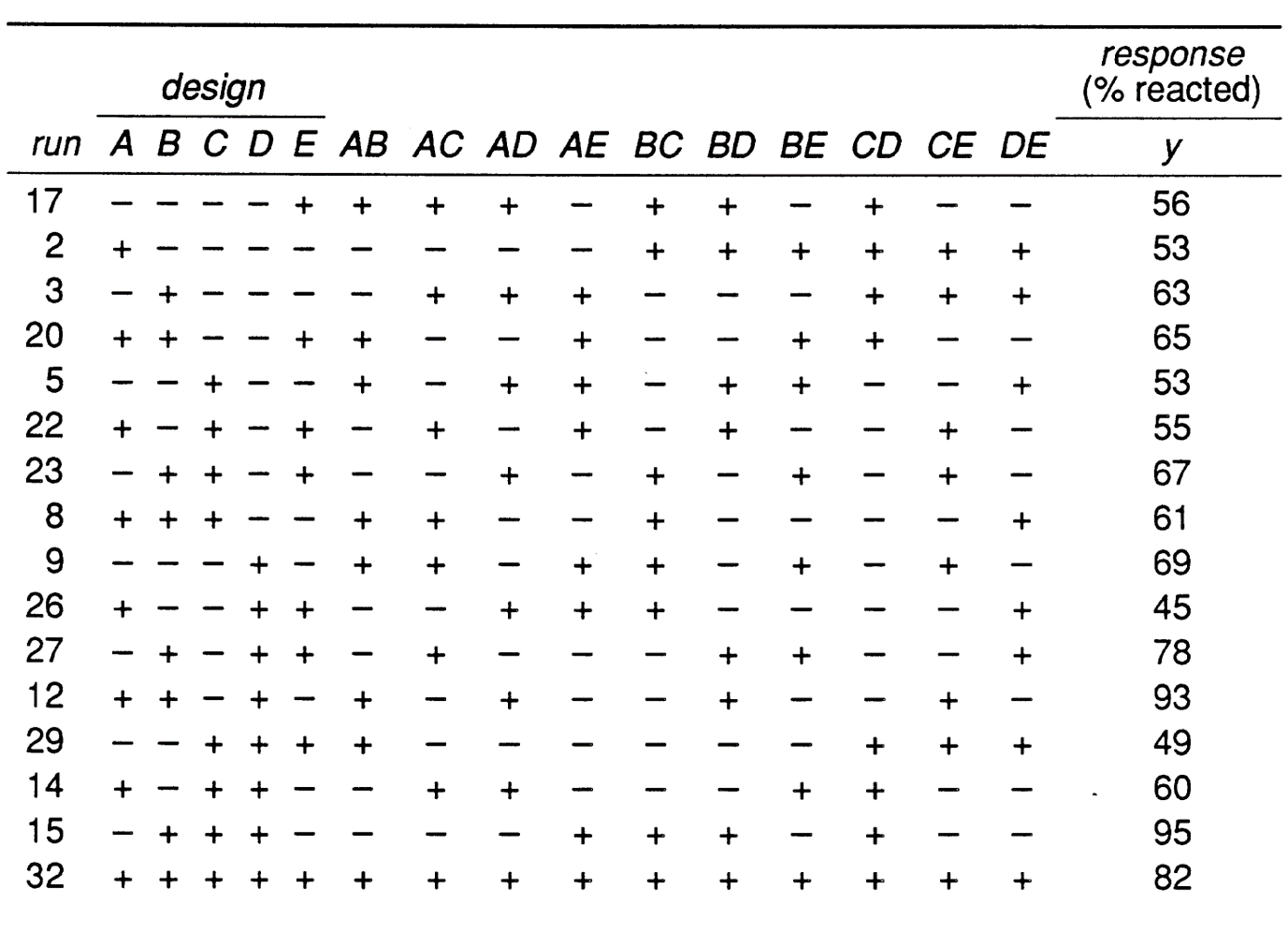
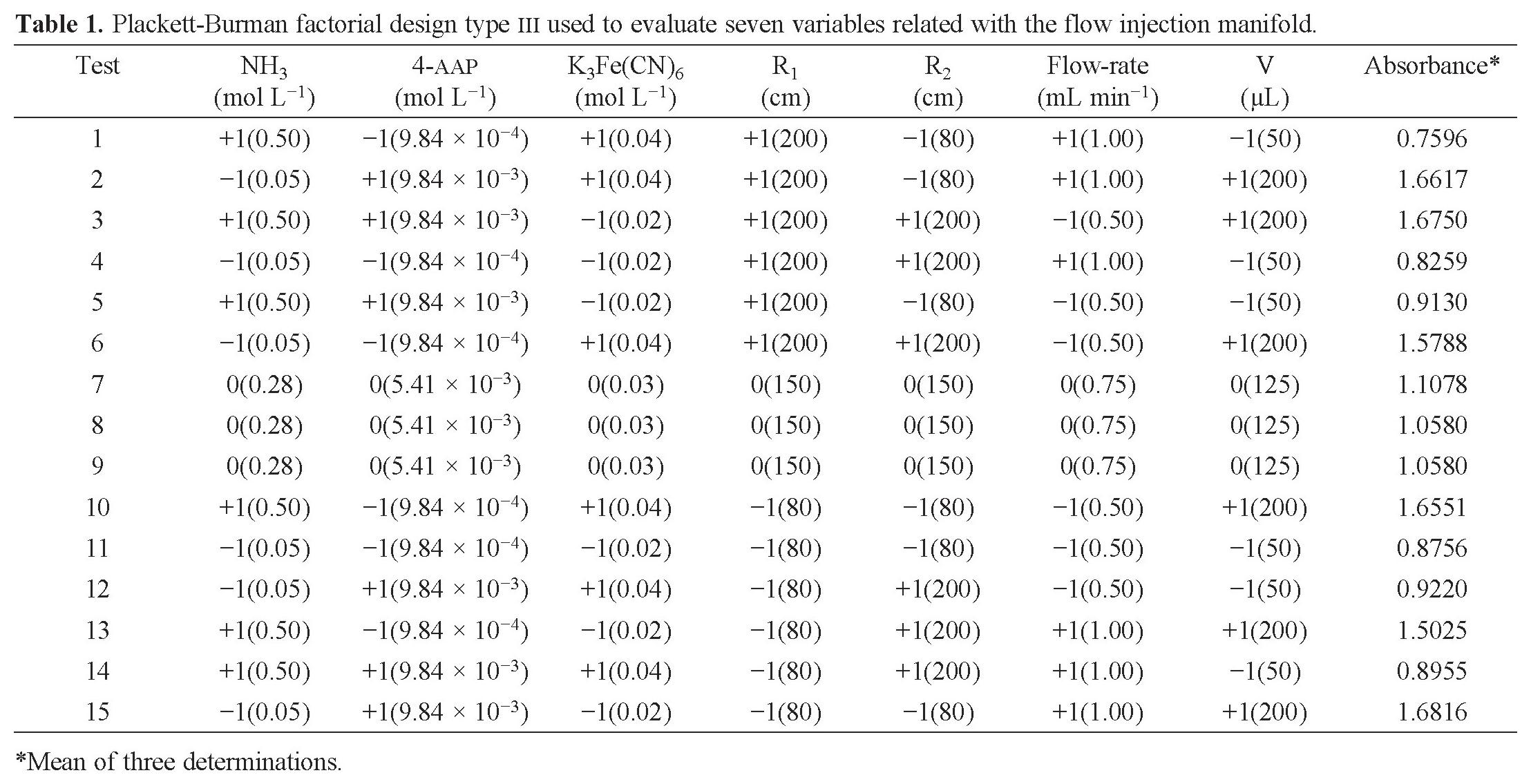
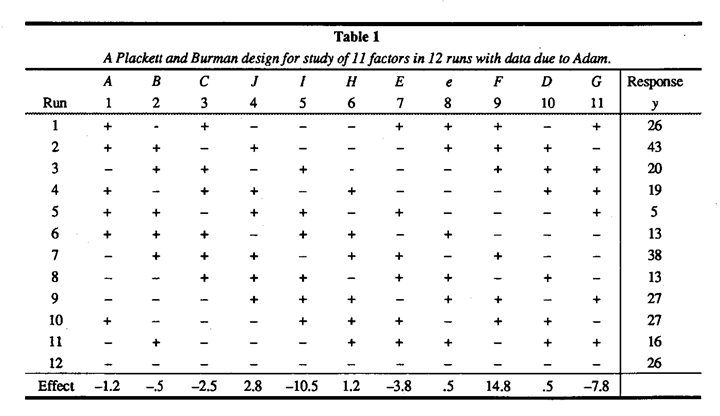
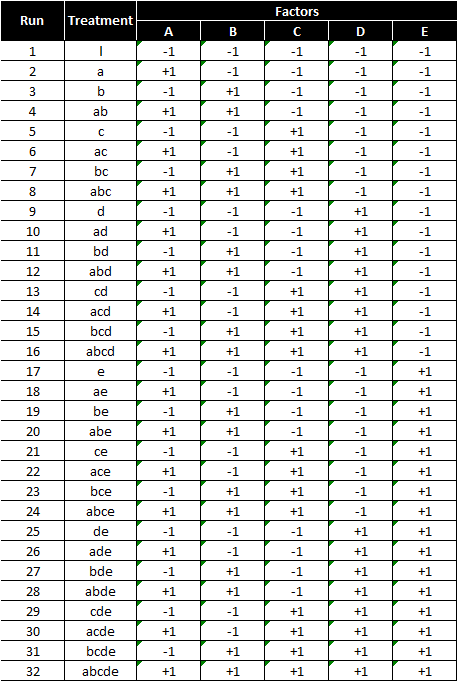
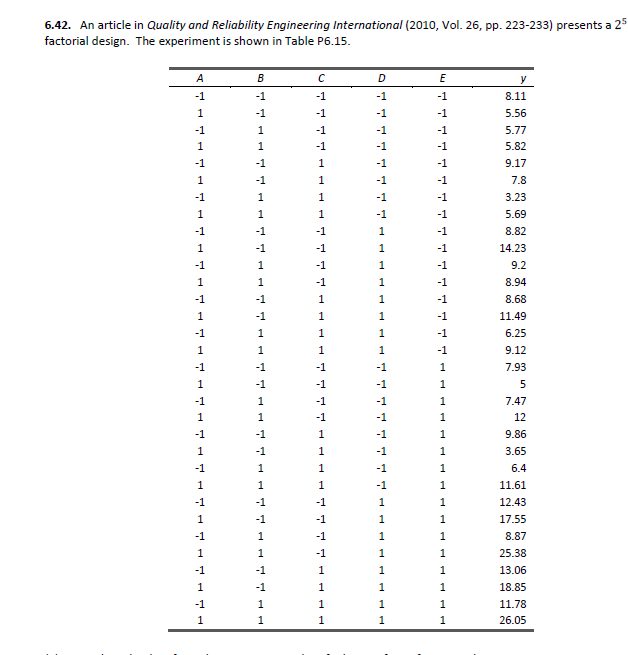
2 5 factorial design table. Number of observations 32 a complete 2 5 factorial design response variable y mean over 15 reps of ceramic strength factor 1 table speed 2 levels. Slow 025 m s and fast 125 m s factor 2 down feed rate 2 levels. Clicking on the 2 r k p specification for a given design provides details courtesy of dataplot files of the design generators the defining relation the confounding structure as far as main effects and two level. A half fraction fractional factorial design would require only half of those runs.
The equivalent one factor at a time ofat experiment is shown at the upper right. In table 7 1 the factorial designs for 2 3 and 4 experimental parameters are shown. If it is not a factorial experiment then is it possible to turn this design into a factorial design. K factors all at two levels require relatively few runs per factor studied very widely used in industrial experimentation interpretation of data can proceed largely by common sense elementary arithmetic and graphics.
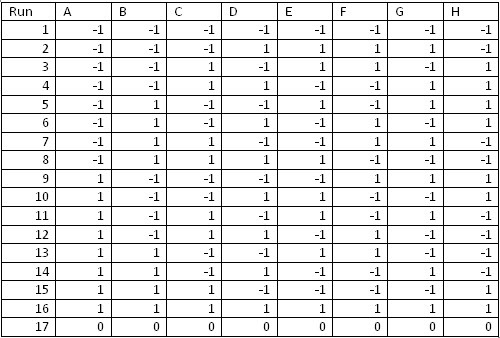
The design table shows the experimental conditions or settings for each of the factors for the design points using coded factor names and levels. With 3 factors that each have 3 levels the design has 27 runs. Factorial designs a simple example. For example in the first run of the experiment factor a is at level 1.
If the experimenter can reasonably assume that certain high order interactions often 3 way. Two level factorial versus one factor at a time ofat. Bhh 2nd ed chap 5 special case of the general factorial design. What is the table of contrasts for a 2 3 factorial design.
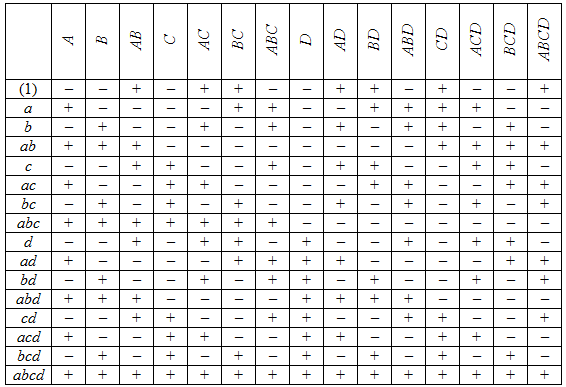
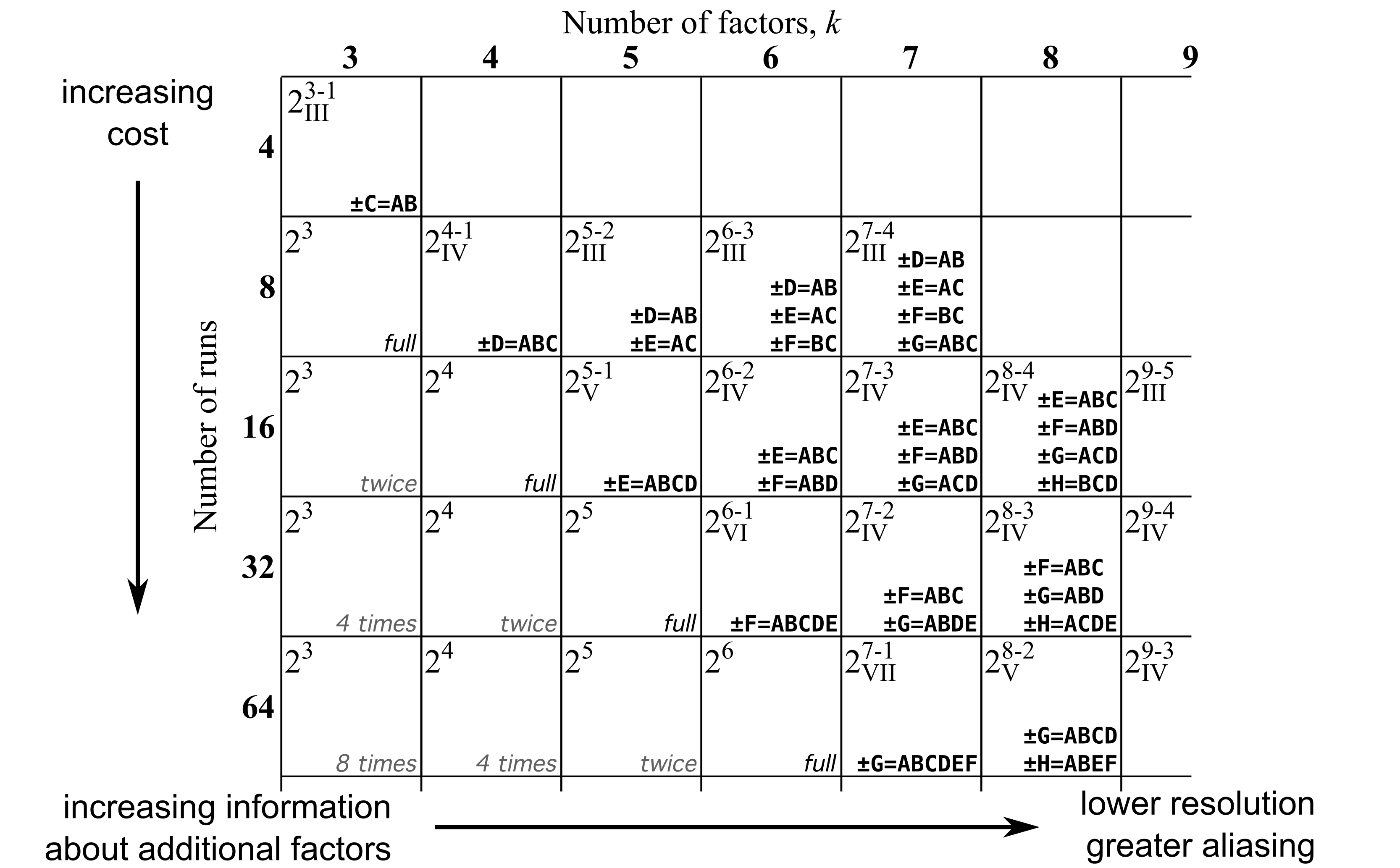
Slow 05 mm and fast 125 mm factor 3 wheel grit 2 levels. The main effects for a and b are 10 and 12 respectively. Table 3 17 catalogs these useful fractional factorial designs using the notation previously described in figure 3 7. The top part of figure 3 1 shows the layout of this two by two design which forms the square x space on the left.
A design with 9 factors requires 512 runs. For example a 2 level full factorial design with 6 factors requires 64 runs. To continue the example with higher numbers six parameters. As the number of factors in a 2 level factorial design increases the number of runs necessary to do a full factorial design increases quickly.
Factors b and c are at level 3. The 2k factorial design montgomery chap 6. The simplest factorial design involves two factors each at two levels. Is this a factorial experiment.
5 two level fractional factorial designs because the number of runs in a 2k factorial design increases rapidly as the number of factors increases it is often impossible to run the full factorial design given available resources.